Unlocking Remote IoT VPC: Best Practices & Benefits
Is the cloud truly the final frontier for the Internet of Things, or are we on the cusp of a more nuanced, secure, and controlled approach? The rise of Remote IoT VPCs Virtual Private Clouds specifically designed for the Internet of Things suggests that the future of IoT might lie in a hybrid model, one that blends the scalability of the cloud with the security and localized control of a dedicated, virtualized infrastructure.
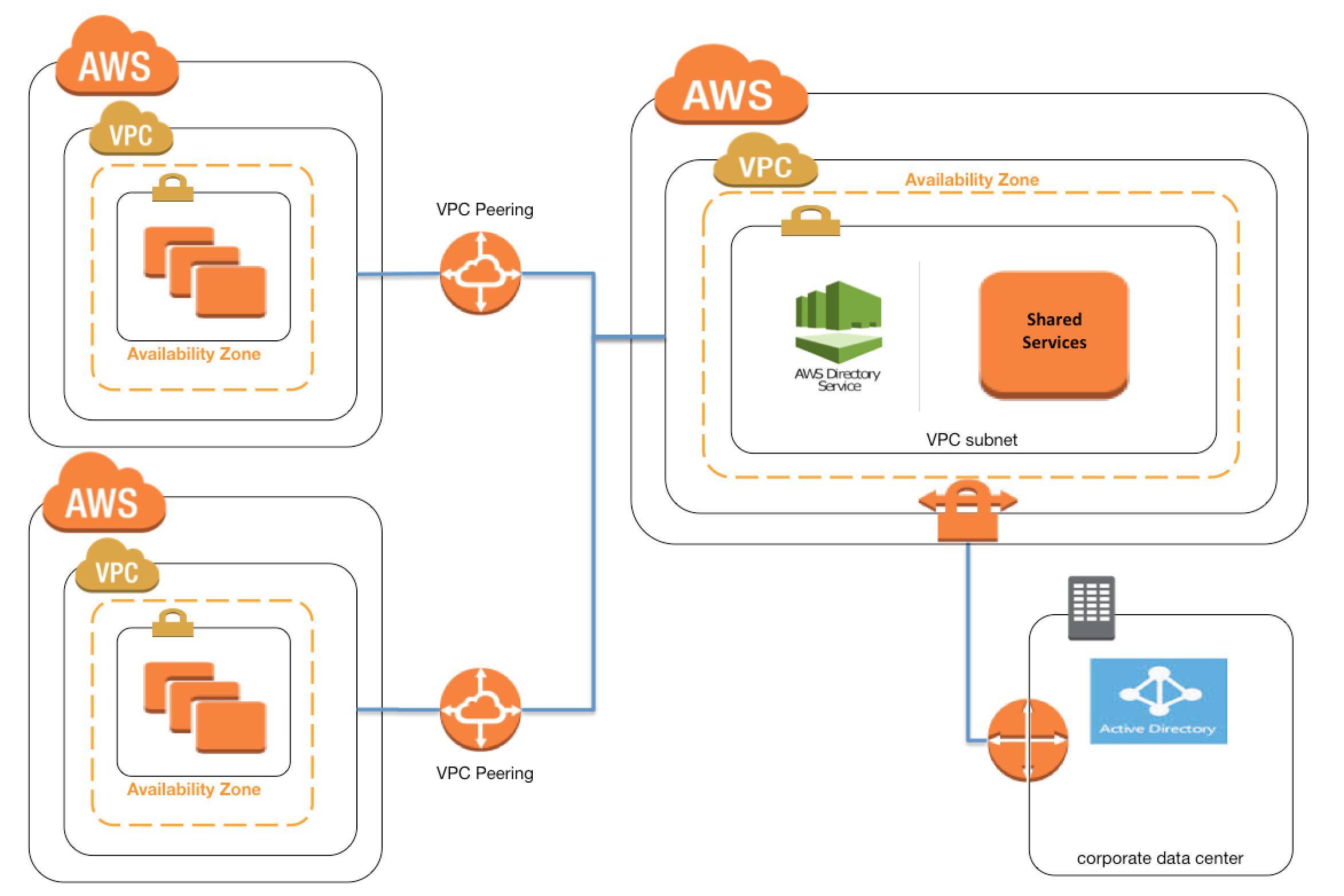
The shift towards Remote IoT VPCs represents a significant evolution in how we manage and secure the ever-expanding landscape of connected devices. Where traditional cloud-based IoT solutions often rely on shared infrastructure and the public internet, Remote IoT VPCs offer a more tailored approach. They provide a virtualized, isolated environment where IoT devices can communicate, process data, and be managed with enhanced security and control. This is particularly crucial in sectors demanding high levels of data privacy, low latency, and regulatory compliance, such as healthcare, finance, and critical infrastructure. The appeal of this architecture also extends to organizations operating in remote or bandwidth-constrained environments, where the ability to perform local processing and reduce reliance on constant internet connectivity is paramount. The term "remoteiot vpc" has become increasingly common.
For those unfamiliar, a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is essentially a private network within a public cloud. It allows organizations to isolate their cloud resources, providing a higher degree of control over their network configuration, security settings, and access controls. A Remote IoT VPC takes this concept a step further, specifically tailoring the VPC to the needs of IoT devices. This includes features like optimized network protocols, support for specific device communication standards (e.g., MQTT, CoAP), and integration with IoT device management platforms. The benefits are numerous. Enhanced security is a primary advantage, with the isolated nature of the VPC reducing the attack surface and mitigating the risk of data breaches. Reduced latency is another critical benefit, as data processing and communication can occur closer to the edge, improving responsiveness and performance. Cost savings can also be realized, particularly in bandwidth-intensive applications, as local processing reduces the need to transmit large volumes of data to the cloud. Remote IoT VPCs are not a simple solution. They represent a paradigm shift in how IoT infrastructure is designed, deployed, and managed. But they do have their challenges, which will be explored in further detail.
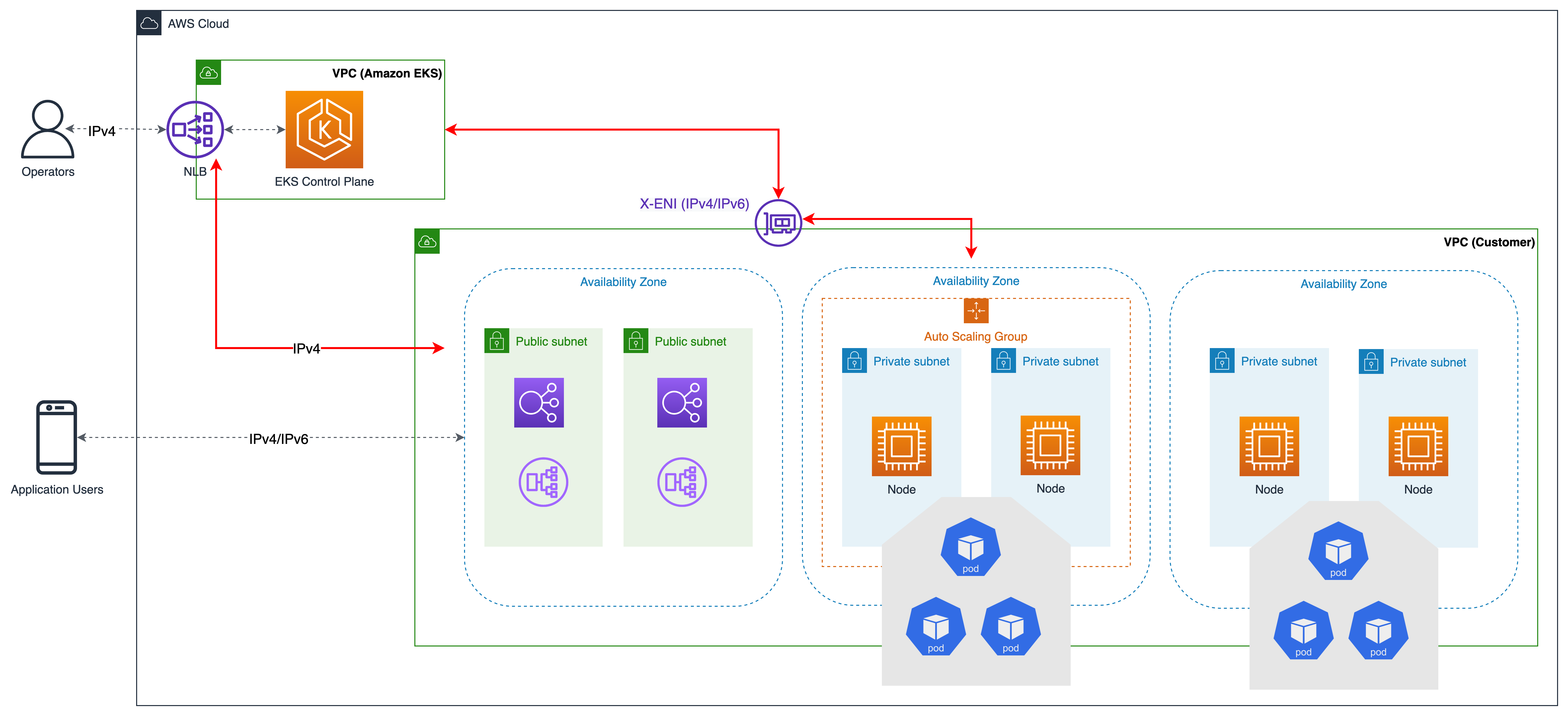
Let's delve into the core architectural principles of a Remote IoT VPC. The fundamental building blocks include:
- Virtualization: At the heart of the Remote IoT VPC is virtualization. This enables the creation of virtual machines (VMs), containers, and other virtualized resources within the VPC. These virtual resources provide the compute, storage, and networking capabilities required to support IoT devices and applications.
- Networking: Sophisticated networking configurations are crucial. This encompasses virtual networks, subnets, routing, and security groups that control the flow of traffic within the VPC and between the VPC and external networks. The goal is to create a secure, isolated network environment tailored to the needs of IoT devices.
- Security: Robust security measures are essential. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and encryption to protect data in transit and at rest. Identity and access management (IAM) is also vital to ensure that only authorized devices and users can access the VPC resources.
- Device Management: The VPC must integrate with device management platforms to enable secure onboarding, monitoring, and control of IoT devices. This may involve the use of device certificates, remote firmware updates, and device health monitoring.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing capabilities may be incorporated to enable data processing and analysis at the edge of the network. This reduces latency and bandwidth consumption, enhancing the responsiveness of IoT applications.
The implementation of a Remote IoT VPC typically involves several steps, from planning and design to deployment and ongoing management.
- Planning and Design: Careful planning is crucial. This involves defining the requirements of the IoT deployment, including the number and type of devices, data processing needs, security requirements, and performance expectations. Based on these requirements, the VPC architecture is designed, including the selection of appropriate cloud services and networking configurations.
- Infrastructure Setup: Once the design is finalized, the infrastructure is set up. This involves provisioning virtual machines, setting up virtual networks, configuring security groups, and installing any necessary software or applications.
- Device Onboarding: IoT devices are onboarded into the VPC. This typically involves provisioning device certificates, configuring network settings, and establishing secure communication channels. Device management platforms are often used to streamline the onboarding process.
- Application Deployment: Applications that process and analyze data from IoT devices are deployed within the VPC. These applications may include data aggregation, analytics, and visualization tools.
- Monitoring and Management: Ongoing monitoring and management are essential. This includes monitoring the performance of the VPC, monitoring device health, managing security settings, and performing regular maintenance.
The advantages of Remote IoT VPCs are manifold, as touched upon earlier. Enhanced security is perhaps the most significant benefit. The isolated nature of the VPC reduces the attack surface, making it more difficult for unauthorized actors to gain access to IoT devices and sensitive data. Data breaches, a constant threat in the interconnected world, are significantly mitigated. Reduced latency is another major advantage. By processing data closer to the source, in the virtual environment of the VPC, response times are dramatically improved. This is critical for time-sensitive applications like industrial automation, smart grids, and autonomous vehicles, where every millisecond counts.
Cost savings, in particular, related to bandwidth optimization, represent another compelling reason for adopting a Remote IoT VPC architecture. By processing data locally and reducing the need to transmit large volumes of data to the cloud, organizations can significantly reduce their bandwidth costs. This is especially beneficial in remote locations or bandwidth-constrained environments. Furthermore, local processing can reduce the reliance on the internet, improving the availability and reliability of IoT applications, and supporting business continuity. Control over data and infrastructure is another compelling benefit. A Remote IoT VPC provides organizations with greater control over their data and infrastructure, enabling them to meet specific regulatory requirements, such as those related to data privacy and sovereignty.
Lets examine how Remote IoT VPCs are being applied in practice. Various industries are already leveraging the power of this technology:
- Healthcare: Remote IoT VPCs enable secure and reliable data transmission from medical devices, improving patient monitoring and care. The sensitive nature of patient data makes the enhanced security features particularly attractive.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, Remote IoT VPCs facilitate real-time monitoring of equipment performance, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency. The low-latency and cost-saving benefits are particularly relevant here.
- Smart Cities: Remote IoT VPCs support the deployment of smart city applications, such as traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety systems. The enhanced security features are crucial for maintaining the integrity of these systems.
- Retail: Remote IoT VPCs improve inventory management, customer experience, and supply chain optimization by securely transmitting data from retail devices.
However, the transition to Remote IoT VPCs is not without its challenges. One significant hurdle is the complexity of design and implementation. Building and managing a Remote IoT VPC requires specialized expertise in cloud computing, networking, security, and IoT device management. Organizations may need to invest in training their existing staff or hire new personnel with the necessary skills. They might look to partners for solutions, from specialist cloud service providers.
Interoperability can be another challenge. Ensuring that different IoT devices and applications can communicate and exchange data within the VPC can be complex. Organizations may need to adopt open standards or develop custom integrations to achieve interoperability. Vendor lock-in is a potential risk if organizations rely too heavily on a single cloud provider. Organizations should carefully evaluate their options and choose a provider that offers the flexibility and portability they need. Integration with existing IT infrastructure can also be challenging. Organizations may need to integrate their Remote IoT VPC with their existing IT systems, such as their enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. This may involve developing custom integrations or leveraging third-party integration tools.
Despite these challenges, the long-term benefits of Remote IoT VPCs are substantial. They represent a more secure, efficient, and controllable way to manage and leverage the power of IoT. As the number of connected devices continues to grow exponentially, the need for a more tailored and secure infrastructure will only increase. The "remoteiot vpc" approach is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the Internet of Things. The initial investment is often met with a positive return in time, improved security and management for remote devices.
Looking ahead, several key trends are likely to shape the evolution of Remote IoT VPCs:
- Edge Computing Integration: Further integration of edge computing capabilities will be crucial, enabling even lower latency and more localized data processing.
- AI and Machine Learning: The use of AI and machine learning to automate the management of IoT devices and applications, including anomaly detection and predictive maintenance, is expected to increase.
- Enhanced Security Features: Continuous advancements in security technologies, such as zero-trust architectures and blockchain-based security solutions, will be integrated to further protect IoT devices and data.
- Simplified Management Tools: The development of user-friendly management tools and platforms will streamline the deployment and management of Remote IoT VPCs.
- Standardization: The adoption of open standards and interoperability protocols will make it easier for organizations to integrate different IoT devices and applications.
The question of whether Remote IoT VPCs are the future of IoT might not have a simple yes or no answer, but one thing is certain: they are a crucial piece of the puzzle. They represent a significant step forward in how we approach the challenges of security, performance, and control in the world of connected devices. As technology continues to evolve, and as the demands for data security and low latency continue to rise, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and innovative solutions emerge in the Remote IoT VPC space. The potential is vast, and the implications are far-reaching, with a constant focus on refining the use of "remoteiot vpc" architecture.